In this blog post, we’ll explore the possibilities of stacking rigid-flex circuit boards and delve into its advantages and limitations.
In recent years, the demand for compact, lightweight and high-performance electronic devices has grown significantly. As a result, engineers and designers are constantly seeking innovative ways to maximize a product’s functionality while minimizing space consumption. One technology that has emerged to address this challenge is rigid-flex circuit boards. But can you stack multiple rigid-flex circuit boards together to create a more compact, more efficient device?
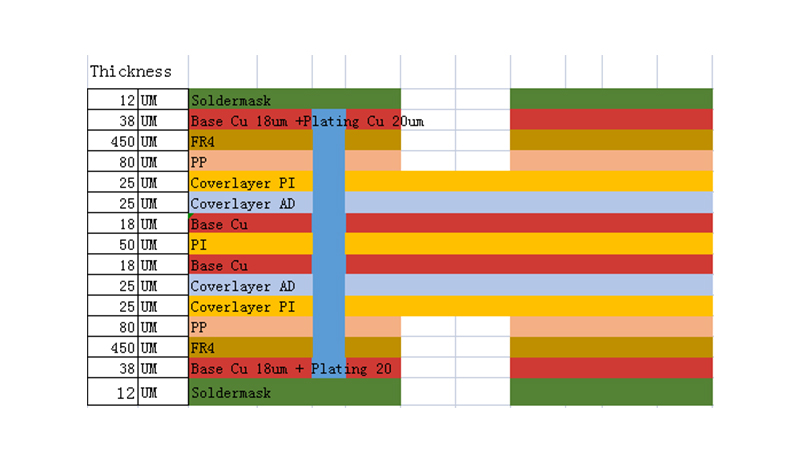
First, let’s understand what rigid-flex circuit boards are and why they are a popular choice in modern electronic design. Rigid-flex circuit boards are a hybrid of rigid and flexible PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards). They are manufactured by combining rigid and flexible circuit layers so that they have both rigid parts for components and connectors and flexible parts for interconnects. This unique structure allows the board to bend, fold or twist, making it ideal for applications requiring complex shapes or layout flexibility.
Now, let’s address the main question at hand – can multiple rigid-flex boards be stacked on top of each other? The answer is yes! Stacking multiple rigid-flex circuit boards offers multiple advantages and opens up new possibilities in electronic design.
One of the main advantages of stacking rigid-flex circuit boards is the ability to increase the density of electronic components without significantly increasing the overall size of the device. By stacking multiple boards together, designers can efficiently utilize available vertical space that would otherwise go unused. This allows the creation of smaller, more compact devices while maintaining a high level of functionality.
Additionally, stacking rigid-flex circuit boards can isolate different functional blocks or modules. By separating parts of the device onto separate boards and then stacking them together, it is easier to troubleshoot and replace individual modules when necessary. This modular approach also simplifies the manufacturing process as each board can be designed, tested and manufactured independently before being stacked together.
Another advantage of stacking rigid-flex boards is that it provides more routing options and flexibility. Each board can have its own unique routing design, optimized for the specific components or circuits it houses. This significantly reduces cabling complexity and optimizes signal integrity, improving overall device performance and reliability.
While there are several advantages to stacking rigid-flex circuit boards, limitations and challenges associated with this approach must be considered. One of the major challenges is the increased complexity of design and manufacturing. Stacking multiple boards adds additional complexity to the design process, requiring careful consideration of interconnections, connectors, and overall mechanical stability. Additionally, the manufacturing process has become more complex, requiring precise alignment and assembly techniques to ensure proper operation of the stacked boards.
Thermal management is another important aspect to consider when stacking rigid-flex circuit boards. Because electronic components generate heat during operation, stacking multiple circuit boards together increases the overall cooling challenge. Proper thermal design, including the use of heat sinks, thermal vents, and other cooling techniques, is critical to preventing overheating and ensuring reliable performance.
All in all, stacking multiple rigid-flex circuit boards together is indeed possible and offers many benefits for compact and high-performance electronic devices. By utilizing additional vertical space, isolation of functional blocks, and optimized routing options, designers can create smaller, more efficient devices without compromising functionality. However, it is important to recognize the increasing complexity of design and manufacturing, as well as the need for proper thermal management.
In summary, the use of stacked rigid-flex circuit boards breaks the boundaries of space utilization and flexibility and revolutionizes electronic design. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovation and optimization of stacking technology, leading to smaller and more powerful electronic devices in the future. So embrace the possibilities offered by stacked rigid-flex circuit boards and let your creativity run wild in a world of compact and efficient electronic design.
Post time: Sep-18-2023
Back