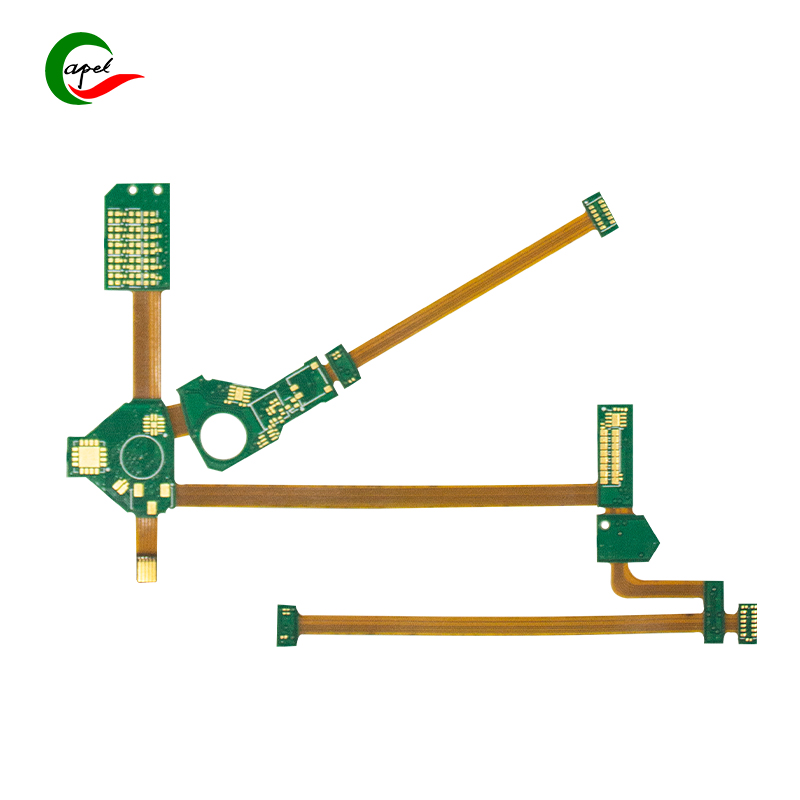
In this blog post, we’ll explore what rigid-flex boards are and how they work.
When it comes to the world of electronic devices, one cannot ignore the importance of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These small but vital components are the backbone of most modern electronic devices. They provide the necessary connections for different components so that they can work together seamlessly. PCB technology has evolved significantly over the years, resulting in various types of circuit boards, including rigid-flex boards.
First, let’s understand the basic concepts of rigid-flex boards. As the name suggests, rigid-flex boards combine rigid and flexible components onto a single circuit board. It offers the best of both types, making it ideal for many applications.
Rigid-flex boards consist of multiple layers of flexible circuit substrates that are interconnected by rigid sections. These flexible substrates are made of polyimide material, which allows them to bend and twist without breaking. The rigid portion, on the other hand, is usually made of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy material, which provides the necessary stability and support.
The combination of rigid and flexible sections provides many benefits. First, it allows for a more compact design because the flexible sections can be bent or folded to fit into tight spaces. This makes rigid-flex boards particularly useful in applications where space is limited, such as mobile devices or wearable technology.
In addition, the use of flexible substrates can improve reliability. Traditional rigid boards can suffer from issues such as solder joint fatigue or mechanical stress due to temperature fluctuations or vibration. The flexibility of the substrate in a rigid-flex board helps absorb these stresses, thereby reducing the risk of failure.
Now that we understand the structure and benefits of rigid-flex boards, let’s take a closer look at how they actually work. Rigid-flex panels are designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Engineers create a virtual representation of the circuit board, defining the layout of components, traces, and vias.
Once the design is complete, it goes through a series of manufacturing processes. The first step involves producing the rigid portion of the circuit board. This is done by laminating together layers of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy material, which are then etched to create the necessary circuit patterns.
Next, the flexible substrate is fabricated. This is accomplished by depositing a thin layer of copper on a piece of polyimide and then etching to create the required circuit traces. Multiple layers of these flexible substrates are then laminated together to form the flexible portion of the board.
Adhesive is then used to bond the rigid and flexible parts together. This adhesive is carefully selected to ensure a strong and reliable connection between the two parts.
After the rigid-flex board is assembled, it goes through various testing processes to ensure its functionality and reliability. These tests include checking continuity, verifying signal integrity, and evaluating the board’s ability to withstand environmental conditions.
Finally, the completed rigid-flex board is ready to be integrated into the electronic device for which it was designed. It is connected to other components using soldering or other connection methods, and the entire assembly is further tested to ensure proper functionality.
In summary, rigid-flex boards are an innovative solution that combines the advantages of rigid and flexible circuit boards. They offer a compact design, increased reliability, and the ability to withstand harsh environments. The manufacturing process involves careful integration of rigid and flexible materials, resulting in versatile and reliable electronic components. As technology continues to advance, we can expect the use of rigid-flex boards to become more widespread across various industries.
Post time: Sep-15-2023
Back