The manufacturing process of 8-layer PCBs involves several key steps that are critical to ensuring the successful production of high-quality and reliable boards. From design layout to final assembly, each step plays a vital role in achieving a functional, durable and efficient PCB.
First, the first step in the 8-layer PCB manufacturing process is design and layout. This involves creating a blueprint of the board, determining the placement of components, and deciding on routing of traces. This stage typically uses design software tools such as Altium Designer or EagleCAD to create a digital representation of the PCB.
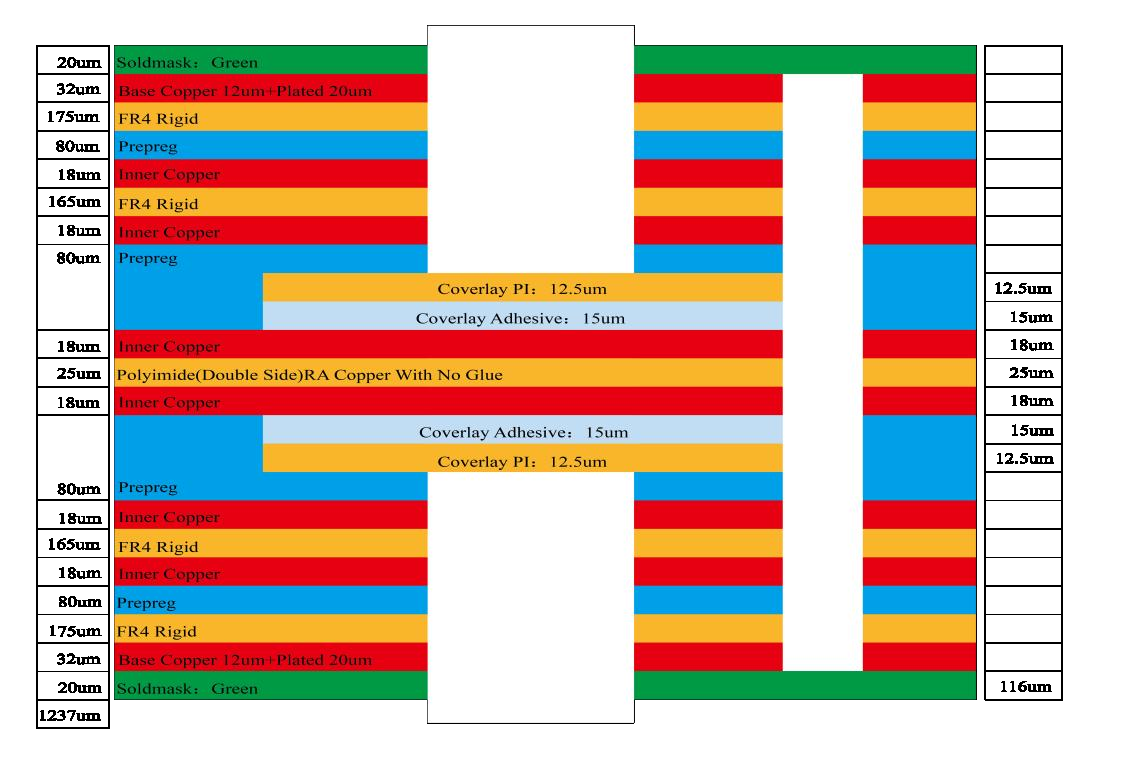
After the design is complete, the next step is the fabrication of the circuit board. The manufacturing process begins with selecting the most suitable substrate material, usually fiberglass-reinforced epoxy, known as FR-4. This material has excellent mechanical strength and insulating properties, making it ideal for PCB manufacturing.
The manufacturing process involves several sub-steps, including etching, layer alignment and drilling. Etching is used to remove excess copper from the substrate, leaving traces and pads behind. Layer alignment is then performed to accurately stack the different layers of the PCB. Precision is crucial during this step to ensure the inner and outer layers are properly aligned.
Drilling is another important step in the 8-layer PCB manufacturing process. It involves drilling precise holes in the PCB to enable electrical connections between different layers. These holes, called vias, can be filled with conductive material to provide connections between layers, thereby enhancing the functionality and reliability of the PCB.
After the manufacturing process is complete, the next step is to apply solder mask and screen printing for component marking. Solder mask is a thin layer of liquid photoimageable polymer used to protect copper traces from oxidation and prevent solder bridges during assembly. The silk screen layer, on the other hand, provides a description of the component, reference designators, and other basic information.
After applying the solder mask and screen printing, the circuit board will go through a process called solder paste screen printing. This step involves using a stencil to deposit a thin layer of solder paste onto the surface of the circuit board. Solder paste consists of metal alloy particles that melt during the reflow soldering process to form a strong and reliable electrical connection between the component and the PCB.
After applying the solder paste, an automated pick-and-place machine is used to mount the components onto the PCB. These machines accurately position components into designated areas based on layout designs. The components are held in place with solder paste, forming temporary mechanical and electrical connections.
The final step in the 8-layer PCB manufacturing process is reflow soldering. The process involves subjecting the entire circuit board to a controlled temperature level, melting the solder paste and permanently bonding the components to the board. The reflow soldering process ensures a strong and reliable electrical connection while avoiding damage to components due to overheating.
After the reflow soldering process is complete, the PCB is thoroughly inspected and tested to ensure its functionality and quality. Perform various tests such as visual inspections, electrical continuity tests, and functional tests to identify any defects or issues.
In summary, the 8-layer PCB manufacturing process involves a series of critical steps that are essential to producing a reliable and efficient board. From design and layout to manufacturing, assembly and testing, each step contributes to the overall quality and functionality of the PCB. By following these steps precisely and with attention to detail, manufacturers can produce high-quality PCBs that meet a variety of application requirements.
Post time: Sep-26-2023
Back