Delamination in PCB can lead to significant performance issues, especially in rigid-flex designs where both rigid and flexible materials are combined. Understanding how to prevent delamination is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of these complex assemblies. This article will explore practical tips for preventing PCB delamination, focusing on PCB lamination, material compatibility, and optimized machining parameters.
Understanding PCB Delamination
Delamination occurs when layers of a PCB separate due to various factors, including thermal stress, moisture absorption, and mechanical strain. In rigid-flex PCBs, the challenge is heightened due to the differing properties of rigid and flexible materials. Therefore, ensuring compatibility between these materials is the first step in preventing delamination.
Ensure PCB Material Compatibility
The choice of materials is critical in preventing delamination. When designing a rigid-flex PCB, it is essential to select materials that have similar thermal expansion coefficients. This compatibility minimizes stress during thermal cycling, which can lead to delamination. Additionally, consider the adhesive used in the lamination process. High-quality adhesives that are specifically designed for rigid-flex applications can significantly enhance the bond strength between layers.
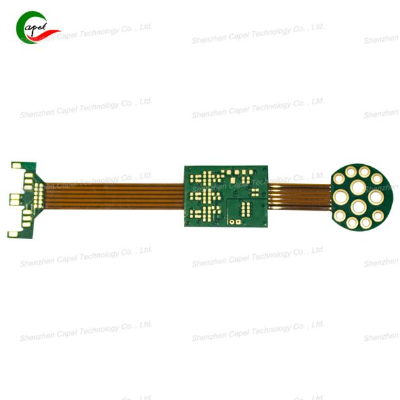

PCB Lamination Process
The lamination process is a pivotal stage in PCB manufacturing. Proper lamination ensures that the layers adhere well to each other, reducing the risk of delamination. Here are some practical tips for effective PCB lamination:
Temperature and Pressure Control: Ensure that the lamination process is conducted at the correct temperature and pressure. Too high a temperature can degrade the materials, while insufficient pressure can lead to poor adhesion.
Vacuum Lamination: Using a vacuum during the lamination process can help eliminate air bubbles that may cause weak spots in the bond. This technique ensures a more uniform pressure across the PCB layers.
Curing Time: Allow adequate curing time for the adhesive to bond properly. Rushing this process can lead to incomplete adhesion, increasing the risk of delamination.
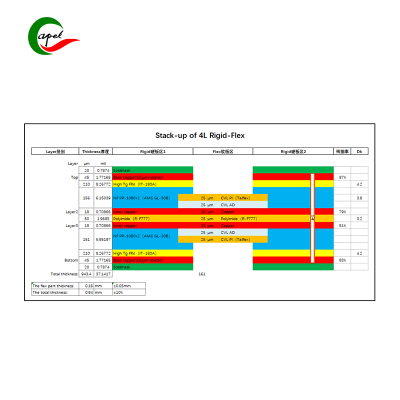
Optimized Rigid-Flex PCB Machining Parameters
Machining parameters play a significant role in the integrity of rigid-flex PCBs. Here are some optimized machining tips to prevent delamination:
Drilling Techniques: Use appropriate drill bits and speeds to minimize heat generation during the drilling process. Excessive heat can weaken the adhesive bond and lead to delamination.
Routing and Cutting: When routing or cutting the PCB, ensure that the tools are sharp and well-maintained. Dull tools can cause excessive pressure and heat, compromising the integrity of the layers.
Edge Treatment: Properly treat the edges of the PCB after machining. This can involve smoothing or sealing the edges to prevent moisture ingress, which can contribute to delamination over time.
Practical Tips for Preventing PCB Delamination
In addition to the above strategies, consider the following practical tips:
Environmental Control: Store PCBs in a controlled environment to prevent moisture absorption. Humidity can weaken the adhesive bond and lead to delamination.
Regular Testing: Implement regular testing of PCBs for signs of delamination during the manufacturing process. Early detection can help mitigate issues before they escalate.
Training and Awareness: Ensure that all personnel involved in the PCB manufacturing process are trained in best practices for lamination and machining. Awareness of the factors that contribute to delamination can lead to better decision-making.

Post time: Oct-31-2024
Back






