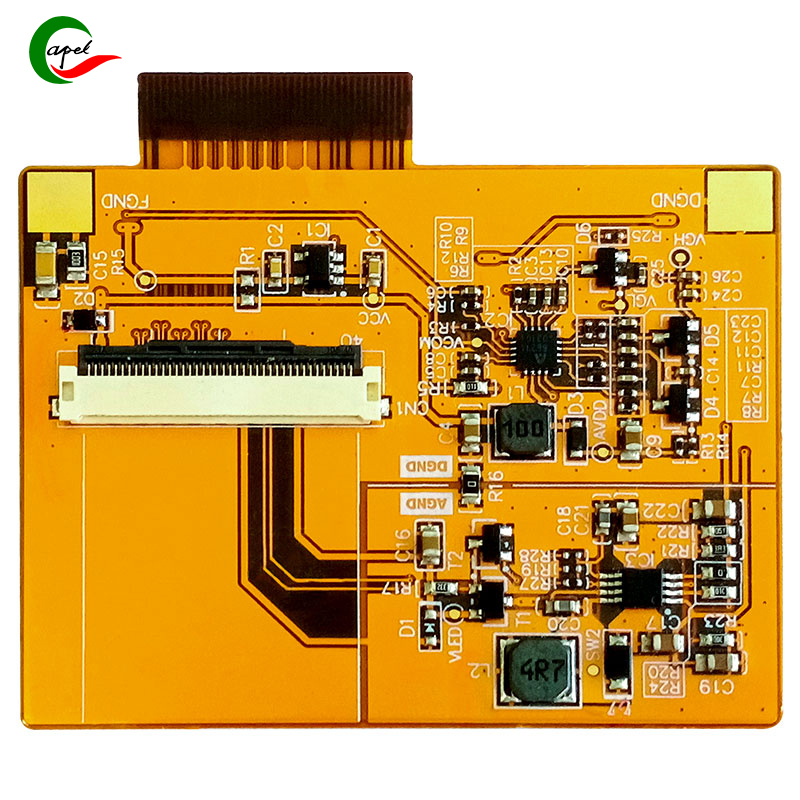
Introduce:
Flexible PCB manufacturing plays a vital role in the electronics manufacturing industry. As technology advances, the demand for flexible PCBs has increased significantly. In this ultimate guide, we’ll explore flexible PCB construction, layout, and stackup types. It is important to understand the following keywords: Flexible PCB Manufacturing, Flexible PCB Structure, Flexible PCB Copper Thickness, Flexible PCB Solder Mask, Flexible PCB Layout, Flexible PCB Adhesive Sheet, and Flexible PCB Layup Types as they are essential for optimizing your product. It’s important.
1. Basic knowledge of flexible PCB manufacturing:
A. Definition and characteristics of flexible board: A flexible PCB, also known as a flexible circuit, is a printed circuit board that can be bent, folded, or twisted without breaking. They offer several advantages over rigid PCBs, including flexibility, lightweight, and durability. These properties make them suitable for a variety of applications, especially those requiring compact and bendable electronics.
B. Flexible PCB structure: The construction process of flexible PCB involves the use of flexible substrates. The most commonly used substrates are polyimide and polyester, which provide the necessary flexibility and insulation properties required for flexible PCBs. These substrates undergo a series of manufacturing steps such as etching, plating, and lamination to create the desired circuit pattern.
C. Understand the copper thickness in flexible PCB: Copper thickness plays a vital role in the performance of flexible PCB. It determines the current carrying capacity, impedance, and flexibility of the PCB. Different copper thickness choices can be made according to the specific requirements of the design. Thicker copper provides higher current carrying capabilities but also reduces PCB flexibility. A proper balance must be struck between these factors to achieve optimal performance.
2. Key components of flexible PCB manufacturing:
A. Flexible PCB solder mask: The solder mask is a protective layer covering the bare copper traces on the PCB. It helps prevent solder bridges, corrosion, and electrical shorts during welding. Flexible PCB uses special solder mask material to ensure flexibility and durability. The flexible PCB solder mask selection and application process requires careful consideration of the PCB design and its intended application.
B. Flexible PCB Layout: A well-designed, flexible PCB layout is critical for optimal performance and reliability. It involves placement of components, routing of traces, and signal integrity considerations. The components must be placed in a way that allows the PCB to bend and bend appropriately. Traces should be routed to minimize stress on the flex areas and ensure efficient signal transmission. Best practices for designing a flexible PCB layout include using curved traces, avoiding sharp angles, and ensuring adequate clearance between traces.
C. Flexible PCB adhesive sheet: An adhesive sheet is used in flexible PCB manufacturing to bond different layers together. It provides mechanical strength, stability, and insulation. There are different types of adhesive sheets available, such as acrylic-based sheets, epoxy-based sheets, and rubber-based sheets. The choice of adhesive sheet depends on factors such as temperature resistance, flexibility requirements, and compatibility with other materials. Choosing the right adhesive sheet is very important to ensure the reliability and durability of your flexible PCB.
3. Flexible PCB stack-up types:
A. Introduction to PCB stackup: PCB stackup refers to the arrangement of different layers in a PCB. In flexible PCB manufacturing, the stack up plays a vital role in signal integrity, impedance control, and thermal management. By carefully selecting and arranging the layers, designers can optimize the performance of flexible PCBs.
B. Common Flexible PCB Layup Types: There are a variety of layup types used in flexible PCB manufacturing, including single-layer, dual-layer, and multi-layer configurations. Each stacking type has its advantages and limitations. Single-layer flexible PCBs are the simplest and most cost-effective option, but they have limited routing capabilities. Double-layer flexible PCB provides more wiring options and can accommodate more complex designs. Multilayer flexible PCBs provide greater routing flexibility, and improved impedance control, and can support higher circuit densities. However, they are more complex and costly to manufacture.
In summary:
In this comprehensive guide, we cover all aspects of flexible PCB manufacturing, including construction, layout, solder mask, adhesive sheets, and stackup types. Understanding these key elements will enable designers to optimize the performance and reliability of their flexible PCB designs. Processes and technologies are critical to the production of flexible PCBs, and by following best practices, manufacturers can ensure the delivery of high-quality, reliable products to meet the needs of the electronics industry.
Post time: Nov-10-2023
Back