Selecting the correct type of printed circuit board (PCB) is critical when designing electronic equipment. Two popular options are flex PCB and traditional PCB. Flexible PCBs are flexible and can be bent or folded to fit unconventional form factors. On the other hand, traditional PCBs are rigid, stable and cost-effective. In this article, we will compare Flex Circuit Pcb and traditional rigid PCBs to help you make an informed decision based on your project requirements.
Table of Contents:
What is a flexible PCB?
What is a traditional PCB?
Advantages of flexible PCB
a.flexibility
b. Dimensions and weight
c.durability
Advantages of traditional PCB
a.cost
b.simple
c.Stablize
Application of flexible PCB
a.Wearable device
b. Aerospace and automotive industries
c.medical equipment
Application of traditional PCB
a.Consumer electronics products
b.Industrial equipment
c.telecommunications
Choose the right PCB for your project
a.Consider Design Specifications
b. Assessing flexibility requirements
c.cost considerations
d. Discuss with PCB manufacturer or engineer
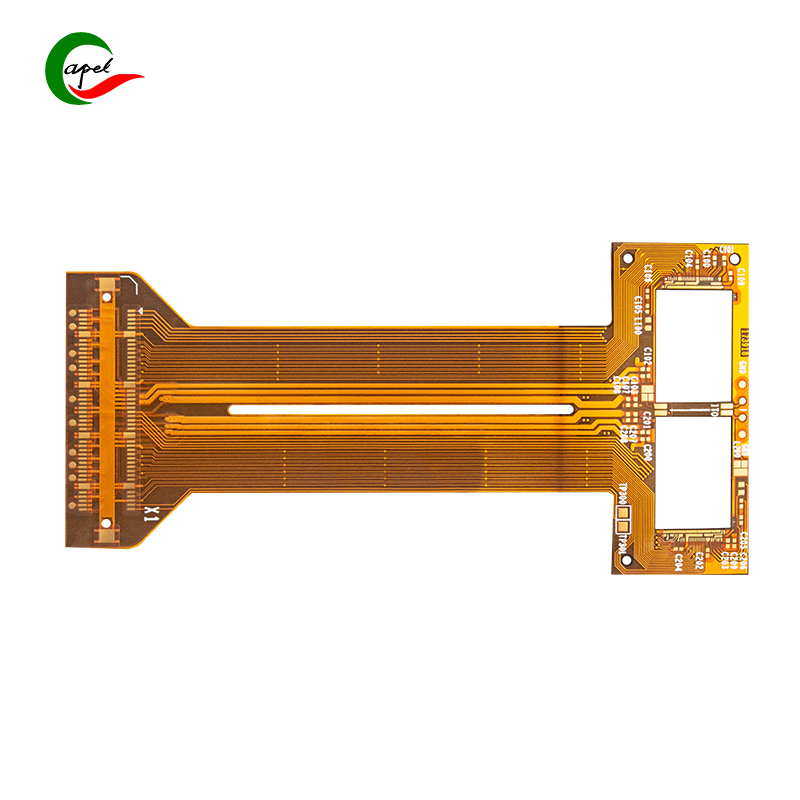
What is a flexible PCB?
Flexible PCBs, also known as flexible printed circuit boards, are designed to be flexible, allowing them to be bent, folded or twisted to fit unique spaces or form factors. They consist of thin, flexible layers of conductive material, such as copper, deposited on a flexible substrate, usually made of polyimide or polyester. Flexible printed circuit boards are manufactured using a specialized process that allows them to withstand repeated bending and flexing without compromising performance or reliability.
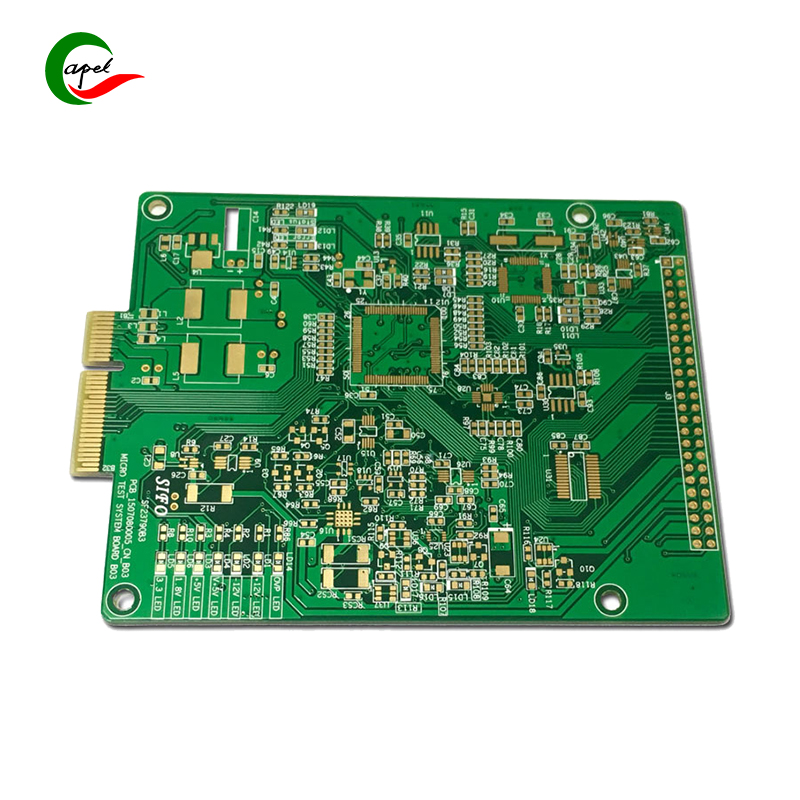
What is a traditional PCB?
Conventional PCBs, or rigid printed circuit boards, are the most commonly used type of PCB. They are made of rigid materials such as fiberglass or epoxy, which provide stability and mechanical strength. Traditional PCBs consist of multiple layers of conductive copper traces etched onto a rigid substrate, enabling the interconnection of various electronic components. While traditional PCBs lack the flexibility of flex PCBs, they are cost-effective and well suited for applications where rigidity and stability are critical.
Advantages of flexible PCB:
Flexible PCBs offer several advantages over traditional PCBs that make them an attractive option for certain projects.
Flexibility: The main advantage of a flexible PCB is the ability to bend and conform to a unique shape or form factor. This flexibility enables you to design equipment that fits into tight spaces or adapts to curved surfaces for greater design freedom.
Size and Weight: Compared to traditional PCBs, flex PCBs are thinner and lighter. This makes them suitable for applications with strict space and weight constraints, such as mobile devices, drones or wearable technology.
Durability: Flex PCBs are designed to withstand mechanical stress, vibration, and temperature changes better than conventional PCBs. This durability makes them ideal for applications subject to harsh environments or constant motion, such as automotive electronics or aerospace systems.
Advantages of traditional rigid PCB:
While flexible PCBs have their advantages, conventional PCBs also offer unique advantages for certain projects.
Cost: Traditional PCBs are usually more cost-effective than flex PCBs. Materials used in traditional PCB manufacturing are more readily available, reducing overall production costs.In addition, the manufacturing process of traditional PCBs is more mature and extensive, further contributing to cost savings.
Simplicity: Compared with flexible PCBs, traditional PCBs are simpler in structure, so they are easier to design and manufacture. They follow a standardized, strict format and can be produced in large quantities, simplifying the production process.
Stability: Traditional PCB provides a stable and reliable circuit. Their rigid construction helps maintain a consistent electrical connection, making them suitable for applications requiring precise signal integrity or high-speed communications.
Application of flexible PCB:
Flexible PCB is widely used in various industries and applications because of its flexible characteristics and unique advantages.
Wearables: Flexible PCBs are often used in wearables such as smart watches or fitness trackers. Their flexibility allows the PCB to conform to the shape of the wearable without compromising functionality.
Aerospace and Automotive Industries: Flexible PCBs are used in the aerospace and automotive industries due to their ability to withstand vibration and temperature changes. They are used in applications such as avionics systems, engine control units or wiring harnesses.
Medical Devices: Flexible PCBs are widely used in medical devices such as pacemakers or insulin pumps. Their flexibility allows PCBs to conform to irregular shapes, making them ideal for implantable or wearable medical technology.
Application of traditional PCB:
Conventional PCBs are well suited for a wide range of applications due to their stability and cost-effectiveness.
Consumer Electronics: Traditional PCBs are widely used in consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets or laptops. The rigid structure of traditional PCBs provides stability and reliability, which are critical for these devices.
Industrial Equipment: Traditional PCBs are used in industrial equipment such as machinery or control systems. They provide the necessary stability and durability required in harsh industrial environments.
Telecommunications: Traditional PCBs are widely used in networking equipment, routers or switches in the telecommunications industry. Its sturdy construction ensures stable and consistent signal transmission.
Select the right PCB for your project:
When choosing between flex PCBs and traditional PCBs, there are several factors to consider in order to make the right choice:
Space constraints: Flexible PCBs offer greater design freedom and flexibility, enabling you to create circuits that bend and conform to a variety of shapes and spaces. This can be very beneficial if you have limited space or need to fit a PCB into a compact or irregularly shaped device. On the other hand, traditional PCBs are more rigid and may not be suitable for space-constrained applications.
Weight and Dimensions: Due to the flexible substrate material, flexible PCBs are usually lighter and thinner than traditional PCBs. If weight and size reduction are important considerations for your project, then a flex PCB might be a better choice.
Manufacturing Complexity: Compared to conventional PCBs, the fabrication of flex PCBs is more complex because of the extra steps involved, such as material preparation and specialized etching processes. This can lead to higher manufacturing costs and longer production cycles. Traditional PCBs, on the other hand, have well-established manufacturing processes and may be more readily available at lower cost.
Environmental Durability: Flexible PCBs are known for their durability and resistance to mechanical stress, vibration and temperature changes. They are suitable for applications that require repeated bending or flexing, making them ideal for products such as wearables, medical devices, and aerospace applications. Conventional PCBs are generally more rigid and may not be able to withstand the same level of mechanical stress or bending.
Rigid component integration: If your project requires the integration of rigid components such as connectors, microcontrollers, or sensors, a traditional PCB may be more suitable. Traditional PCBs provide a solid platform for mounting and securing rigid components, while flexible PCBs may require additional support or structural reinforcement.
Consider Design Specifications: Evaluate the project’s specific design requirements and constraints. If you need a PCB that can bend or conform to a unique shape, flex PCBs are the obvious choice. However, if rigidity and stability are more important, a traditional PCB may be a better choice.
Evaluate Flexibility Requirements: Consider whether your project really needs the flexibility that flex PCBs provide. If your design does not require bending or folding capabilities, a traditional PCB may be a more cost-effective and straightforward choice.
Cost Considerations: Budget is an important consideration for any project. Conventional PCBs are generally less expensive than flex PCBs, making them an economical choice for cost-constrained projects.
Discuss with PCB Manufacturer or Engineer: Seek advice from a PCB manufacturer or an experienced engineer to better understand the pros and cons of each type of PCB for your specific project. They can guide you through the selection process based on their expertise and experience.
In conclusion:
the choice between flex PCB and traditional PCB depends on the specific requirements and constraints of your project. If you need flexibility, miniaturization, and high signal integrity, a flex PCB might be a better choice. On the other hand, if your project involves conventional electronics with lower cost constraints, conventional PCBs are still a solid choice. It is always recommended to consult a PCB manufacturer and design specialist to determine the best solution for your project.
Shenzhen Capel Technology Co., Ltd. has been focusing on the circuit board industry for 15 years. Whether it is flexible PCB board, flex-rigid pcb, rigid board or SMT assembly, Capel has provided professional technical support for our customer’s projects, and we have solved countless project problems. The expert team broke through and successfully promoted the smooth completion of the project, which seized the opportunity for the customer’s project in the market.
Post time: Aug-22-2023
Back