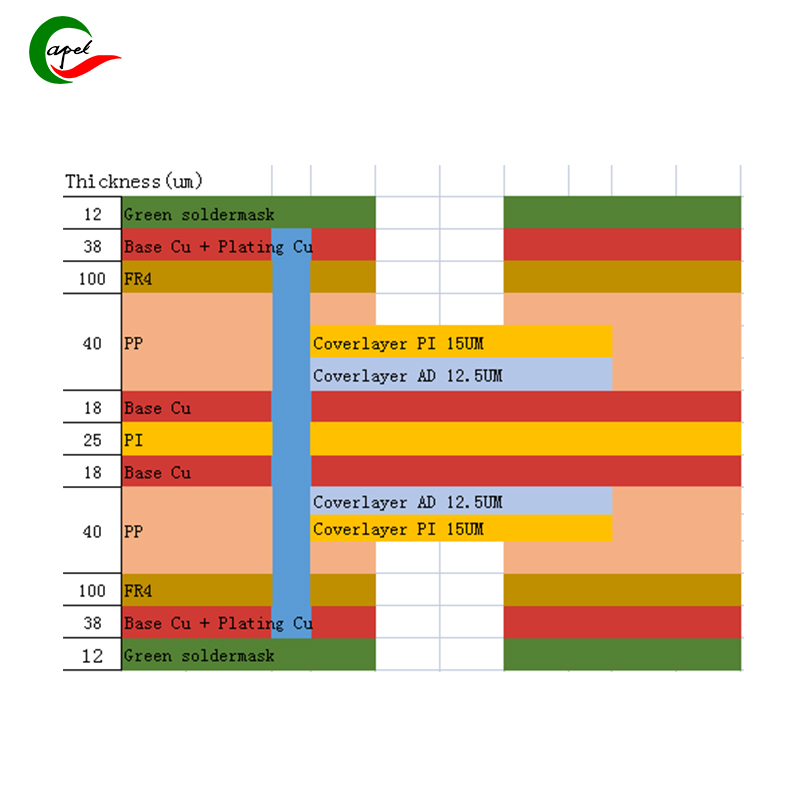
Rigid-flex circuit boards are becoming more and more popular due to their unique design, which combines the advantages of rigid and flex PCBs. As electronic devices become more compact and complex, engineers continue to push the limits of these boards. An important factor in the design and complexity of a rigid-flex circuit board is the number of layers it can accommodate. Here we’ll dig into this topic and answer the question: What is the maximum number of layers for a rigid-flex board?
Understanding Rigid-Flex Boards:
Before delving into the maximum number of layers, we first have an understanding of rigid-flex circuit boards. Rigid-flex circuit boards, as the name suggests, are circuit boards that combine rigid and flexible substrates in their structure. This unique design can increase the versatility and durability of electronic devices. The board’s flexible areas allow it to bend and fold, making it suitable for applications where space is limited or where equipment may be subjected to harsh conditions.
Rigid areas, on the other hand, provide stability and support for components that require a solid mounting surface. By combining these two types of substrates, rigid-flex boards offer a seamless integration of flexibility and rigidity, resulting in compact and reliable solutions for various electronic devices.
A key advantage of rigid-flex boards is the elimination of connectors and cables, reducing cost and assembly time. Integrating the flexible area directly into the board allows direct connection of components, resulting in a more compact and robust system
From the application point of view, rigid-flex boards are widely used in aerospace, medical, automotive, consumer electronics and other industries. In aerospace applications, for example, they are used in aircraft control systems where the combination of flexibility and rigidity allows for easy installation in confined spaces while ensuring reliable performance in challenging environments.
The effect of the number of layers on the rigid-flex circuit board:
The number of layers in a rigid-flex board has a significant impact on its design and overall functionality. Each layer serves a specific purpose and adds to the complexity of the board. The more layers, the more complex the board, which can increase the functionality and flexibility of the design.
A big advantage of having more layers is the ability to accommodate more components and traces. Each additional layer creates more space for traces, improving signal integrity and reducing electromagnetic interference. This is especially important for high-speed applications where signal quality and noise reduction are critical.
In addition, the greater number of layers allows for the inclusion of dedicated layers such as signal, ground, and power planes. These planes provide a low-impedance path for signals and minimize noise and interference, helping to improve board stability and performance. The more layers available, the more options there are to add these dedicated planes, resulting in better overall board performance.
Additionally, the increased number of layers provides greater flexibility in component placement and routing. It effectively separates different circuit parts, reducing signal crosstalk and ensuring optimal signal flow. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in complex circuit designs that require the integration of multiple components into a compact space.
It is worth noting, however, that adding layers also presents certain challenges. The manufacturing process becomes more complex and expensive, as each layer requires additional manufacturing steps and precise alignment during lamination. Therefore, the cost of producing a rigid-flex board increases with each additional layer.
Factors Affecting the Maximum Number of Layers:
There are several factors to consider when determining the maximum number of layers a rigid-flex board can accommodate:
First, the complexity of the circuit design plays an important role. More complex designs with greater numbers of components and interconnects typically require more layers to efficiently route signals and avoid interference. Complex designs may involve multiple signal, power and ground planes, as well as dedicated layers for specific functions, all of which contribute to the total layer count.
Space constraints within electronic devices also limit the number of layers. Smaller devices have limited space, which can limit the number of layers that can be incorporated into a design. Designers need to optimize the number of layers to fit the available space while meeting the functional requirements of the device.
Manufacturing capacity is another factor affecting the maximum number of layers. The manufacturing process of rigid-flex boards involves multiple steps, including interlayer bonding and lamination processes. Each additional layer adds complexity to the manufacturing process, requiring precise alignment and bonding techniques to ensure board integrity. Manufacturers need to consider their manufacturing capabilities and ensure they can produce boards with the required number of layers within their capacity and quality standards.
Signal integrity is critical in electronic devices, and the number of layers directly affects signal integrity. As the number of layers increases, so does the possibility of signal interference and crosstalk. Careful engineering and design considerations are critical to minimizing signal integrity issues when incorporating more layers. Proper impedance control, signal routing techniques, and the use of dedicated planes can help mitigate signal integrity issues.
Other factors that may affect the maximum number of layers include cost considerations and reliability requirements. Increasing the number of layers adds to the manufacturing cost of rigid-flex due to the extra steps and materials involved. Designers and manufacturers need to strike a balance between meeting the required layer count and managing the cost impact. Additionally, the reliability requirements of the device may dictate a specific maximum number of layers to ensure long-term performance and durability of the board.
The maximum number of layers for rigid-flex circuit boards depends on a variety of factors, including complexity, space constraints, manufacturability, and signal integrity requirements. While there may not be a clear answer, it is imperative to work closely with an experienced designer and manufacturer to ensure that the number of layers selected meets the needs of the intended application. As technology advances, we can expect the maximum number of layers to continue to evolve, allowing for more innovative and complex electronic devices.
Shenzhen Capel Technology Co., Ltd.established its own rigid flex pcb factory in 2009 and it is a professional Flex Rigid Pcb Manufacturer. With 15 years of rich project experience, rigorous process flow, excellent technical capabilities, advanced automation equipment,comprehensive quality control system, and Capel has a professional experts team to provide global customers with high-precision, high-quality 1-32 layer rigid flex board, hdi Rigid Flex Pcb, Rigid Flex Pcb Fabrication, rigid-flex pcb assembly,fast turn rigid flex pcb,quick turn pcb prototypes.Our responsive pre-sales and after-sales technical services and timely delivery enable our clients to quickly seize market opportunities for their projects.
Post time: Aug-28-2023
Back