In the world of printed circuit boards (PCBs), the term “semi-flex” is quickly gaining acceptance. But what exactly is a semi-flex PCB, and how is it different from other PCB types? This comprehensive guide aims to uncover the fascinating world of semi-flex PCBs, revealing their unique features, benefits and applications. From a detailed explanation of their construction to highlighting their importance in various industries, this blog will give you insight into semi-flex PCBs and why they are becoming increasingly popular in today’s highly advanced technology environment.
1.What is a semi-flexible PCB?
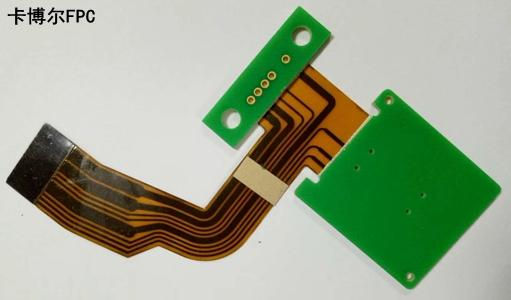
Semi-flex PCBs are specialized printed circuit boards designed to achieve a balance between flexibility and rigidity. Unlike full-flex or rigid PCBs, they can only bend within certain limits, hence the name semi-flex PCBs. Constructed from a combination of rigid and flexible materials, these panels provide a unique combination of structural stability and limited bending capability. The flexible areas within the semi-flex PCB are created using a polyimide-based substrate that provides the necessary flexibility while ensuring durability and high temperature resistance.
2.Construction and design considerations:
To better understand semi-flex PCBs, it is crucial to grasp their complex structure and design. These PCBs are built with multiple layers, just like standard rigid PCBs. The rigid layer is usually composed of FR-4 material, while the flexible layer is made of polyimide. Flex areas combined with copper traces and plated through holes ensure electrical connectivity throughout the PCB.
Design considerations are critical to the successful implementation of semi-flex PCBs. Engineers need to carefully analyze specific application requirements, such as degree of flex, reliability, and resistance to environmental factors. Determining the proper number of layers, material selection, and copper thickness is critical to achieving the ideal balance between rigidity and flexibility.
3.Advantages of semi-flex PCB:
Semi-flex PCBs offer several advantages over traditional rigid PCBs and full-flex PCBs. Let’s explore some of their key advantages:
1. Space optimization: With its unique combination of rigidity and flexibility, semi-flexible PCBs can effectively utilize the available space. They can be folded or bent to fit compact designs, ideal for size-constrained applications.
2. Enhanced durability: The rigid part of the semi-flexible PCB provides structural stability and robustness, enhancing its ability to withstand various mechanical stresses and vibrations better than full-flexible PCBs.
3. Cost-effective solution: Semi-flex PCBs are often a cost-effective alternative to full-flex PCBs, enabling manufacturers to provide reliable flex solutions within budget.
4. Improved reliability: The construction of semi-flexible PCBs minimizes the risk of cracking or breaking because the flexible parts are confined within the specified bending limits. This ensures higher reliability and lifetime, making them suitable for applications requiring long periods of use.
4.Application of semi-flexible PCB:
Semi-flexible PCBs are widely used in many industries due to their unique combination of flexibility and rigidity. Some notable applications include:
1. Medical devices: Semi-flexible PCBs are widely used in portable medical devices such as wearable health monitors, patient tracking devices, and ambulatory devices. Their flexible nature allows for a comfortable fit while maintaining the necessary rigidity for reliable performance.
2. Automotive electronics: The rugged construction and compact size of semi-flex PCBs make them ideal for automotive applications. They are widely used in dashboard controls, infotainment systems and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
3. Aerospace and Defense: The aerospace and defense industry uses semi-flexible PCBs in mission-critical components, including avionics, radar systems, and satellite communications equipment. These PCBs can withstand the harsh environments encountered in these fields while providing much-needed design flexibility.
4. Consumer Electronics: The consumer electronics market has adopted semi-flexible PCBs in smartphones, tablets, and other portable electronic devices. Their ability to fit into tight spaces and withstand repeated folding makes them ideal for these applications.
Conclusion:
Semi-flex PCBs represent a significant development in the field of printed circuit boards, offering a unique combination of flexibility and rigidity. Unlike full-flex or rigid PCBs, semi-flex PCBs strike a perfect balance, making them increasingly popular in various industries. By understanding the construction, design considerations, benefits and applications of semi-flex PCBs, engineers and manufacturers can realize the full potential of semi-flex PCBs. As technology continues to advance, semi-flexible PCBs will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping the future of electronic equipment, ensuring optimum performance and maximizing space utilization.
Post time: Sep-02-2023
Back